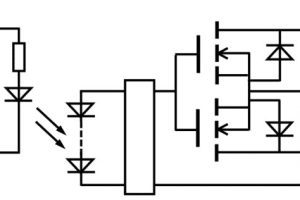
Called TLP241BP, it can switch ac or dc though its single isolate 280mΩ (max) output switch – implemented as a pair of back to back mosfets – and handle pulses up to 4.2A (100ms, 1/10 duty).
Output leakage is 1μA max at 40V (25°C), 10μA max at 60V and increases rapidly above 70V.
Input-to-output isolation is 5kVrms, and the relay can operate across -40 to +110°C although output current needs to be derated at -14mA/°C from 25°C upwards.
 Recommended input current to operate the output is 7 – 14mA (~1.65V at 10mA), with an absolute maximum of 20mA detated above 97°C.
Recommended input current to operate the output is 7 – 14mA (~1.65V at 10mA), with an absolute maximum of 20mA detated above 97°C.
Turn-on time is typically 400μs (1.4ms max) and turn-off is in 30μs (500μs max).
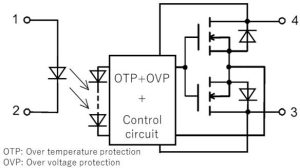
Over-temperature protection latches the output off when internal temperature exceeds 145°C, requiring lower temperature and the LED’s input current to be removed briefly before the output will turn on again.
Output over-voltage protection clamps the output somewhere between 80 and 100V, but is only for brief surges (10μs is the test duration) and the device will be damaged if over-voltage persists – it is not protected by the over-temperature circuit during over-voltage.
The device is UL-recognised, cUL-recognised and, only if option ‘D4’ is specified, VDE-approved (EN 60747-5-5).
The pitch of the package is 7.62mm and offers 7mm creepage and clearance – a second device, TLP241BPF, has 10.16mm pitch package with 8mm creepage and clearance. In both cases, the internal isolation thickness is 0.4mm.
The devices are general-purpose, Toshiba sees them being used in building management, sensors, I/O interfaces and battery management.
Find the TLP241BP product page here
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News