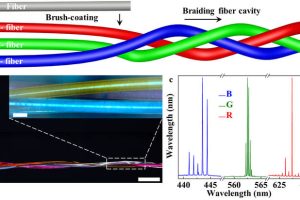
Beijing University of Technology has created red-green-blue lasing using three optical fibres coated with dye-doped polymer. Each whispering gallery fibre supports multiple lasing modes, with their colour defined by brushing on dye-doped polymer ink. Before weaving together, each fibre has a lower excitation threshold of 19.1μJ/cm2, narrowest spectral line width of 0.045nm and Q (quality factor) of 104, according to ...
Research
The latest electronics research news from within the industry and universities from around the world.
Micromachined wafers make featherweight x-ray lenses for space telescopes
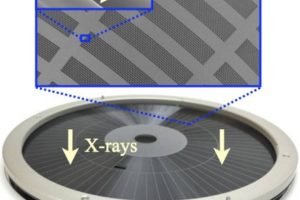
To cut weight from x-ray space telescopes, Tokyo Metropolitan University is micro-machining x-ray lenses from silicon. The lenses exploit the nature of x-rays, which can reflect if they approach a flat surface almost parallel to it, at a slight glancing angle. The Tokyo x-ray lens is machined from a 100mm silicon wafer using reactive ion etching to produce circular slots ...
Imec’s options to reduce metal line resistance at tight pitches
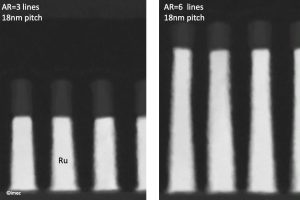
Imec has presented options to reduce the metal line resistance at tight metal pitches, mitigating the resistance/capacitance (RC) increase of future interconnects using direct metal patterning. For the first time, high aspect ratio (AR=6) processing of ruthenium (Ru) in a semi-damascene fashion is experimentally shown to result in about 40% resistance reduction without sacrificing area. Additional simulations confirm the benefits ...
Updated: Owl inspires neuromorphic computation power saving
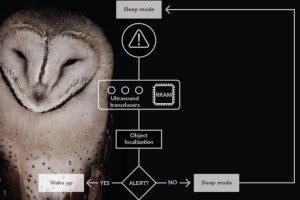
French research lab CAE-Leti has developed a sonic event-driven object-localisation system using analogue in-memory neuromorphic computation, inspired by a barn owl’s brain. “Real-world sensory-processing applications require compact, low-latency, and low-power computing systems,” according to CEA-Leti. “Enabled by their in-memory, event-driven computing abilities, hybrid memristive-CMOS neuromorphic architectures provide an ideal hardware substrate for such tasks.” In the owl, the difference between arrival ...
Cardiff University innovation hub opens its doors
The Translational Research Hub (TRH), designed to foster collaboration between industry and scientists, has officially opened at Cardif University. It is the home of the Institute for Compound Semiconductors (ICS) and Cardiff Catalysis Institute (CCI), and was funded by UK and Welsh governments – including £17.3m through UKRPIF, £12m from Welsh Government, £13.1m in European funding administered by WEFO and ...
ABB and CERN partner to study electric motor energy savings
CERN and ABB are to study electric motor energy use at CERN, and will publish the results for public use. ABB described the project as “non-commercial” and said that it will demonstrate how data insight and service expertise can be applied to make better decisions about saving energy and increasing reliability at large-scale research facilities. “Currently, motors used to power ...
UKRI funding boost for semiconductor R&D at National Epitaxy Facility
The National Epitaxy Facility, a collaboration between the Universities of Sheffield, Cambridge and UCL for semiconductor R&D, has been awarded a further £12 million in funding. The funding, from UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), is to enable semiconductor research and development, in both UK academia and industry, over the next five years. Sheffield University says it will be a critical ...
SiFive opens Cambridge R&D centre
SiFive has opened a UK R&D centre in Cambridge. The company plans to hire over 100 people. “As part of our global expansion, we’re proud to open our UK R&D Centre in Cambridge to access the considerable local technical talent, especially CPU experts,” said Patrick Little, CEO and Chairman, SiFive, “with long-term plans to grow talent and teams in Cambridge and ...
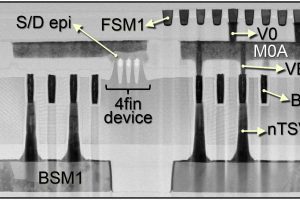
Imec’s backside power delivery for logic
Imec has presented an experimental demonstration of a routing scheme for logic ICs with backside power delivery enabled through nano-through-silicon-vias (nTSVs) landing on buried power rails (BPRs). The BPRs connect to scaled FinFET devices whose performance was not impacted by backside wafer processing. The novel routing scheme with decoupled power and signal wiring acts as a scaling booster for future ...
That robot finger with living skin
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have grown a skin-like layered material from bio-materials found in human skin. The result, demonstrated on a robot finger, self-fits to the underlying structure, is flexible, soft to the touch, and shows some self-healing properties. A 3D printed three-jointed finger, later operated by nylon threads running through it, was used as a scaffold for ‘skin’ ...
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News