Designer viruses may one day produce nano-scale logic. Or so speculated one of two researchers sharing their thoughts ahead of...
Device R&D
Windows generate electricity
Oxford Photovoltaics has been spun out of the University of Oxford to develop solar cell windows. From the Clarendon lab, its fundamental technology is a screen-printable...
Gas sensor uses InAs nanowires
European research labs IMEC and Holst Centre have developed a nanowire sensor that can detect NO2, possibly to concentrations under 100ppb. The sensor’s active components are...
Finger-powered wireless piezo switch
Swiss company Algra is developing a finger-powered piezo wireless push button, aiming it at stick-on light switches and other building control applications. The technology, dubbed Dynapic, is based on low-movement piezo...
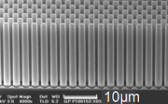
MEMS bring micro DNA analyser closer
Building blocks for a DNA analysing micromachine have been presented at the International Electron Devices Meeting in San Francisco. There is a high-pressure pump, a MEMS filter optimised for DNA separation, and...
IEDM: MEMS resonator breaks Q record
Panasonic and IMEC have developed a MEMS resonator with record Q-factor, presenting it the International Electron Devices Meeting in San Francisco. "MEMS resonators offer...
Fraunhofer Institutes tackle autonomous submarines
Four Fraunhofer Institutes are pooling resources to cut the size and price of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). AUVs are not cheap. "For the time being, the technology is too expensive to...
EU project makes photonics on CMOS line
The European HELIOS project has demonstrated a laser and a 10Gbit/s silicon modulator using CMOS fab-compatible processing. In its second year and co-ordinated by French lab CEA-Leti, the project is developing building blocks...
Brain probe reads and writes individual neurons
Partners in the European NeuroProbes programme have created a probe that can record and stimulate single neurons in the brain. "To discriminate single neurons in the brain, the recording electrode should be positioned very close...
Vital signs measured from a distance
Japanese scientists have recorded heartbeat and breathing remotely using microwaves. The work could lead to the development of non-invasive, real-time stress and clinical sensing...
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News