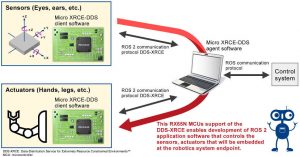
Specifically an XRCE-DDS client (‘Micro XRCE-DDS’ from eProsima) has been implemented on Renesas’ 32bit RX65N MCUs.
“Robot Operating System – ROS – is a key framework that provides libraries and tools that enable developers to bring innovations to the robotics community,” said the firm. “There has been new interest in extending ROS access to embedded MCUs, which accelerates the development of service robots. The development of the ROS 2 addresses these needs. Support of DDS-XRCE enables development of software that controls the sensors and actuators that will be embedded at robotics system endpoints, such as welfare, safe guard, reception, cleaning and household robots.”
In a demonstration, Renesas linked two RX65N-based boards using DDS-XRCE, a sensor board acting as robot eyes and ears, and an actuator board operating its hands and legs. According to the firm, software used in this demonstration will be open-sourced later this year.
According to eProsima’s GitHub page:
Micro XRCE-DDS implements a client-server protocol to enable resource-constrained devices (clients here) to take part in DDS communications – Micro XRCE-DDS Agent (server) makes this communication possible.
Micro XRCE-DDS Agent acts on behalf of the Micro XRCE-DDS Clients and enables them to take part as DDS publishers and/or subscribers in the DDS global data space (GDS).
Micro XRCE-DDS provides both its Agent and an API layer which allows the implementation of its Clients.
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News