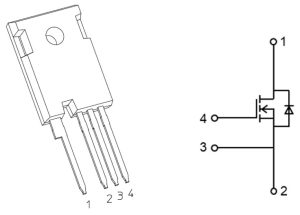
“Devices in the TWxxxZxxxC series are the first Toshiba SiC products to be housed in a TO-247-4L(X) package with a fourth pin,” according to the company. “This allows the provision of a Kelvin connection of the signal source terminal for the gate drive, thereby reducing the parasitic inductance effects of the internal source wire and improving high-speed switching performance.”
Selecting the new TW045Z120C, it is said to have ~40% better turn-on loss and ~34% turn-off loss compared with its existing three-pin TO-247 TW045N120C.
Within TWxxxZxxxC, there are five 650V and five 1200V mosfets, with typical drain-source on-resistance ranging from 15mΩ to 140mΩ. “Combined with low gate-drain charge values, it will enable low losses even in high frequency applications,” is claimed. Maximum continuous drain currents within the family is 100A.
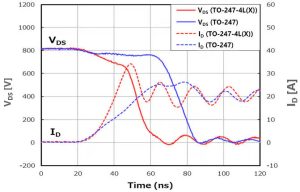 Switch-on with three or four pin packages (800Vdd, 20A Id, 0-18Vgs, 4.7Ω Rg, 25°C, 100μH load)
Switch-on with three or four pin packages (800Vdd, 20A Id, 0-18Vgs, 4.7Ω Rg, 25°C, 100μH load)
Picking the 1.2kV TW045Z120C mentioned, this is a 40A (25°C, 30A continuous or 82A pulsed at 100°C), 45mΩtyp (67mΩtyp 150°C) device.
Gate drain charge is 8.9nC, gate-source charge is 21nC, and total gate charge is 57nC.
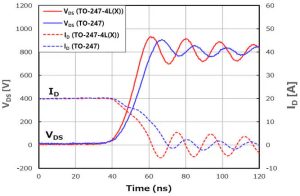
And switching off
Reverse recovery charge and time are 297nC and 54ns, with a current peak of 11A (800V, 13A, 1kA/μs, Vg=0V).
The package is rated for up to 182W and the channel can run up to 175°C – channel to case resistance is 0.824°C/W.
Industrial switching PSU applications are foreseen for the family, in servers, data centres, electric vehicle chargers, photovoltaic inverters and uninterruptible supplies.
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News