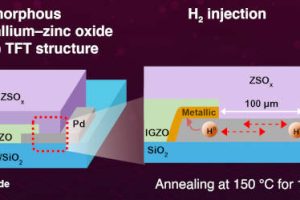
Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology have found a novel way to reduce source and drain contact resistance, and increase carrier mobility, in amorphous oxide transistors. In particular, they are amorphous indium gallium oxide (a-IGZO) thin-film transistors that are being proposed for a form of DRAM, where memory density can be increased by stacking the transistors. The problem is ...
Tag Archives: Tokyo
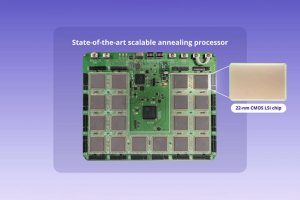
Scalable, fully-coupled annealing processor with 4096 spins accelerates problem-solving
Researchers at the Tokyo University of Science have designed a scalable, fully-coupled annealing processor with 4096 spins, with parallelized capabilities for accelerated problem-solving Annealing processors are designed specifically for addressing combinatorial optimisation problems, where the task is to find the best solution from a finite set of possibilities. With CMOS ICs it is necessary for the components of annealing processors ...
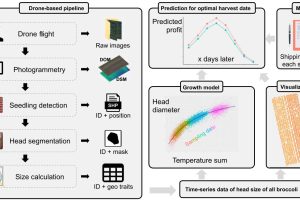
Use drones and AI for more profitable brussels sprouts
The University of Tokyo has demonstrated a near-autonomous drone-based system to identify the perfect day to pick a crop. “Harvesting a field as little as a day before or after the optimal time could reduce the potential income of that field for the farmer by 3.7% to as much as 20.4%,” said Tokyo researcher Wei Guo. “But optimum harvest times ...
2V blue OLED will work on Li-ion batteries
Tokyo Institute of Technology has demonstrated a blue OLED with a forward voltage of 1.97V at 100cd/m2, and still emitting at lower voltages such as 1.5V (right). “Conventional blue OLEDs typically require around 4V for a luminance of 100cd/m2, this is higher than the industrial target of 3.7 V – the voltage of lithium-ion batteries,” according to the Institute. Its ...
2D ferroelectric memory transistor demonstrated
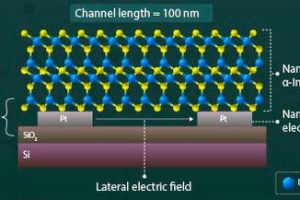
Researchers at Tokyo Tech have made a lateral ferroelectric memory transistor using a 2D material. They picked α-In2Se3, which is “renowned for high carrier mobility, tunable bandgap and strong ferroelectric properties at the atomic level, making it ideal for high-speed memory applications”, according to the university. The bottom-contact transistor has been made by dropping a flake (~29nm thick) of α-In2Se3 ...
Designer solid electrolytes for no-liquid lithium metal batteries
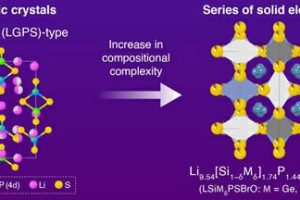
Tokyo Institute of Technology has created a strategy to produce high ionic conductivity solid electrolytes for all-solid-state batteries with lithium metal electrodes. Such solid batteries could offer better battery safety – lithium metal (as opposed to lithium-ion) liquid electrolyte batteries have a poor safety record – but inferior ion conductivity is hampering their development. Inferior conductivity can be intrinsic to ...
VLSI Symposium: 100GHz transceiver for 6G comms
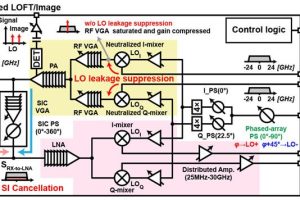
Tokyo Institute of Technology has created a Sub-THz 6G transceiver, which will be revealed next week at the VLSI Symposium. Capable of transmission and reception at over 100GHz, and at 112Gbit/s, “by effectively suppressing the self-interference caused by the transmission signal leaking into the receiver, the proposed architecture reaches unprecedented data rates while maintaining a surprisingly compact size”, according to ...
Promising proton conductor for ceramic fuel cells
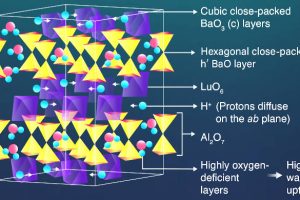
Tokyo Institute of Technology scientist have discovered a promising proton conductor for protonic ceramic fuel cells. Ba2LuAlO5 “has a remarkably high proton conductivity, even without any additional chemical modifications”, according to the university. Protonic ceramic fuel cells use solid proton-conducting ceramic electrolytes and operate between 300 and 600°C. This compares to over 700°C for better-established solid-oxide fuel cells – where ...
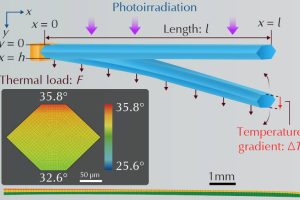
Photothermal resonance for micro-actuators?
Researchers in Japan have exploited resonance to get large amplitude motion from rod-like microcrystals, in a way that could be useful in soft robotics according to Waseda University. Using UV light, they set out to bend a particular type of 2,4-dinitroanisole crystals – chosen because of their large thermal expansion coefficient. The UV wavelength selected matches an absorption peak in ...
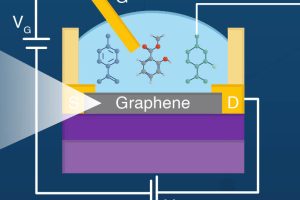
Designer molecules turn graphene FETs into your custom electronic nose
Graphene FETs could make designer electronic noses, following research at Tokyo Tech. This kind of transistor has a channel made from the 2D material graphene, which has high electron mobility that can be modulated in various ways. The channel’s sensitivity to being gated by outside influences has led GFETs, as they are known, to be used in various types of ...
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News